Chapter 9 and 11 Worksheet Answers Biology Review
SELINA Solutions for Grade 10 Biological science Affiliate 9 - The Excretory System
Affiliate 9 - The Excretory System Exercise Ex. 1
Question A.one
Excretion primarily involves
(a) Removal of all byproducts during catabolism
(b) Removal of byproducts during anabolism
(c) Removal of nitrogenous wastes
(d) Throwing out backlog of water
Solution A.ane
(c) Removal of nitrogenous wastes
Question A.ii
Maximum amount of water from the glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed in
(a) Proximal convoluted tubule
(b) Descending limb of loop of Henle
(c) Ascending limb of loop of Henle
(d) Distal convoluted tubule
Solution A.2
(a) Proximal convoluted tubule
Question A.3
Which 1 of the following in real sense is non an excretory activity?
(a) Giving out carbon dioxide
(b) Passing out faecal affair
(c) Sweating
(d) Removal of urea
Solution A.3
(c) Sweating
Question A.4
In humans, urea is formed in
(a) Ureter
(b) Liver
(c) Spleen
(d) kidney
Solution A.four
Liver
Question B.1
Name the following:
(a) The outer region of kidney containing the Bowman'due south capsule.
(b) The tuft of capillaries inside the Bowman'southward capsule.
(c) The function of kidney tubules where the term urine is first used for the fluid in it.
(d) The organ which filters urea.
(east) The organ through which urea is released outside the body of a man being.
(f) The specific pigment plant in urine.
Solution B.1
(a) Cortex
(b) Glomerulus
(c) Distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
(d) Kidney
(eastward) Urethra
(f) Urochrome
Question B.two
Given below are two sets (a and b) of five terms each. Rewrite the terms in their correct order and so every bit to exist in logical sequence.
(a) Afferent arteriole, renal vein, capillary network, glomerulus, efferent arteriole
(b) Renal artery, urethra, ureter, kidney, urinary bladder
Solution B.2
(a) Afferent arteriole, glomerulus, efferent arteriole, capillary network, renal vein
(b) Renal artery, kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra
Question B.3
In each of the following sets of body parts/substances/processes, pick out the one item which overall includes the remaining four
(a) Glomerular filtrate, Bowman'south capsule, ultrafiltration, glomerulus, blood plasma.
(b) Skin, liver, lungs, kidneys, excretion.
(c) ADH, water, pituitary, osmoregulation, urine.
(d) CO2, bile pigments, water, excretion, urea.
Solution B.three
(a) Ultrafiltration
(b) Excretion
(c) Osmoregulation
(d) Excretion
Question B.4
Name the diseases caused due to the post-obit abnormal constituents in urine:
| Abnormal constituents | Diseases |
| (a) Claret | ………………………. |
| (b) Glucose | ………………………. |
| (c) Albumin | ………………………. |
| (d) Bile pigments | ………………………. |
Solution B.4
| Abnormal constituents | Diseases |
| (a) Blood | Haematuria |
| (b) Glucose | Glycosuria |
| (c) Albumin | Albuminuria |
| (d) Bile pigments | Anaemia, hepatitis (jaundice), liver cirrhosis |
Question C.1
Write downwards the functional action of the following parts:
(a) Glomerulus
(b) Henle'southward loop
(c) Ureter
(d) Renal artery
(east) Urethra
Solution C.1
(a) Glomerulus is involved in the procedure of ultrafiltration.The liquid part of the claret which is plasma including urea, salts, glucose filters out from the glomerulus into the renal tubule.
(b) Henle's loop is involved in reabsorption of water and sodium ions.
(c) Ureter carries urine to the urinary bladder by ureteral peristalsis.
(d) Renal artery supplied claret to the kidney.
(e) Urethra is involved in the procedure of micturition i.e. expelling urine out of the body.
Question C.2
Lucifer the items in Column I with those in Column II and write down the matching pairs.
| Column I | Cavalcade II |
| (a) Bowman's Capsule | (i) Renal artery |
| (b) Contains more CO2 and less urea | (ii) Regulates amount of water excreted |
| (c) Anti-diuretic hormone | (iii) Renal vein |
| (d) Contains more urea | (four) Glomerulus |
Solution C.2
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Bowman's Sheathing | Glomerulus |
| (b) Contains more than CO2 and less urea | Renal Vein |
| (c) Anti-diuretic hormone | Regulates amount of water excreted |
| (d) Contains more urea | Renal avenue |
Question C.3
Fill in the blanks in the following passage to make it a meaningful description.
In a nephron, the _______ flows through the ________ nether nifty pressure. The reason for this peachy pressure is that the ________ (outgoing) _________ is narrower than the __________ (incoming). This high force per unit area causes the _______ office of the blood to filter out from the ________ into the _______ sheathing.
Solution C.3
In a nephron, the blood flows through the glomerulus nether great pressure. The reason for this bang-up pressure is that the efferent (outgoing) arteriole is narrower than the afferent arteriole (incoming). This high pressure causes the liquid part of the claret to filter out from the glomerulus into the renal capsule.
Question C.4
Name the post-obit:
(a) Three nitrogenous wastes of our body.
(b) Three organic wastes of our trunk.
(c) Three inorganic wastes of our body.
(d) Three master parts of our urinary system.
(e) Six main parts of nephron.
(f) Three stages of urine germination.
(g) Three types of fluids in unlike parts of a nephron.
Solution C.four
(a) Iii nitrogenous wastes of our body:
1. Urea
ii. Uric acrid
3. Ammonia
(b) Three organic wastes of our body:
1. Urea
2. Uric acrid
three. Creatinine
(c) Three inorganic wastes of our torso:
i. Mutual salt (NaCl)
two. Iron
3. Calcium
(d) Three main parts of our urinary system:
ane. Kidney
two. Urinary bladder
three. Ureter
(eastward) Six primary parts of nephron:
1. Bowman'southward capsule
2. Glomerulus
3. Renal capsule
four. Proximal convoluted tubule (Percentage)
5. Loop of Henle
6. Distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
(f) Three stages of urine formation:
i. Ultrafiltration
2. Reabsorption
three. Tubular secretion
(chiliad) 3 types of fluids in different parts of a nephron:
ane. Glomerular filtrate
2. Glomerular filtrate with glucose and sodium
3. Urine
Question C.5
Choose the odd one out in each of the following sets and write the category for the remaining terms:
(a) Kidney, ureter, neuron, urethra, urinary bladder
(b) Ammonia, urea, backlog sodium chloride, uric acid
(c) Cortex, medulla, loop of Henle, hilum
(d) Glomerulus, collecting duct, papilla, Bowman'due south capsule
Solution C.5
(a) Odd term: Neuron, Category: Others are parts of the human excretory system.
(b) Odd term: Excess sodium chloride, Category: Others are organic nitrogenous wastes.
(c) Odd term: Loop of Henle, Category: Others are parts of the internal structure of kidney.
(d) Odd term: Papilla, Category: Others are parts of the kidney tubule or nephron.
Question C.6
Write full forms of the following abbreviations:
(a) Pct: ……………………….
(b) DCT: ……………………….
(c) ADH: ……………………….
(d) ORS: ……………………….
Solution C.6
(a) PCT: Proximal Convoluted Tubule
(b) DCT: Distal Convoluted Tubule
(c) ADH: Antidiuretic hormone
(d) ORS: Oral Rehydration Solution
Question C.7
Write the exact location of each of the post-obit:
(a) Kidney
(b) Uriniferous tubule
(c) Malpighian capsule
(d) Loop of Henle
Solution C.7
(a) Kidney: It is located on either side of the backbone and protected by the last two ribs.
(b) Uriniferous tubule: Uriniferous tubule begins in the cortex; the tubule dips down to the medulla, then return to the cortex before draining into the collecting duct.
(c) Malpighian sheathing: It comprises of Bowman's capsule and glomerulus and is located in the kidney tubule.
(d) Loop of Henle: It runs in the medulla to plough back and to re-enter the cortex to proceed into the next convoluted region of the tubule.
Question D.ane
Define the following terms:
(a) Excretion
(b) Kidney
(c) Micturition
(d) Osmoregulation
Solution D.1
(a) Excretion: The process of removal of chemic wastes peculiarly nitrogenous waste matter from the trunk is known equally excretion.
(b) Kidney: Kidneys are primary excretory organs eliminating nitrogenous wastes mainly urea from the blood and throwing it out of the torso in the form of urine.
(c) Micturition: The procedure of expelling urine out of the body through urethra by opening the sphincter muscles passing of urine involving relaxation of sphincter muscles between the urinary float and urethra is called micturition.
(d) Osmoregulation: Osmoregulation is a process of maintaining the blood composition of the body i.e. the normal osmotic concentration of water and salts in the trunk.
Question D.two
Differentiate betwixt the following pairs of terms:
(a) Bowman's capsule and Malpighian capsule (structure)
(b) Diuresis and Uremia (cause and problem)
(c) Renal cortex and Renal medulla (location and appearance)
(d) Renal pelvis and Renal papilla (construction)
(e) Urea and urine
(f) Excretion and secretion (utility)
Solution D.2
(a) Differences between Bowman'due south capsule and Malpighian capsule (structure):
| Bowman'southward capsule | Malpighian sheathing |
| Bowman's capsule is a thin walled cup containing the glomerulus. | The Bowman's sheathing along with the knot-like mass of claret capillaries called glomerulus together are known as malpighian capsule. |
(b) Differences between diuresis and uremia (cause and trouble):
| Diuresis | Uremia |
| Diuresis results in increased production of urine due to less secretion of ADH. | Uremia is the accumulation of high quantities of urea in claret due to inability of the kidneys to filter out wastes. |
(c) Differences between renal cortex and renal medulla (location and appearance):
| Renal cortex | Renal medulla |
| The renal cortex is the outer darker region of the kidney. | The renal medulla is the inner lighter region of the kidney. |
(d) Differences between renal pelvis and renal papilla (structure):
| Renal pelvis | Renal papilla |
| The renal pelvis is the expanded front stop of the ureter in the kidney. | The renal papilla is the apex of the renal pyramid which projects into the pelvis. |
(eastward) Differences betwixt urea and urine:
| Urea | Urine |
| Urea is the master excretory product which is excreted in the class of urine. | Urine is the filtrate left afterwards reabsorption and tubular secretion which contains 95% h2o and 5% solid wastes. |
(f) Differences betwixt excretion and secretion (utility):
| Excretion | Secretion |
| Excretion helps in the removal of chemical wastes especially nitrogenous wastes from the body. | Secretion helps in the passage of substances such as potassium and big number of strange chemicals and drugs in the forming urine. |
Question D.3
Give reason/explain:
(a) Excretion is a necessary process of our body.
(b) If we donate one kidney to a needy patient, would it crusade whatever harm to us.
(c) We urinate fewer times in summer than in winter and the urine passed is generally thicker.
Solution D.three
(a) Excretion helps in removing toxic wastes from our body and it also plays an of import role in osmoregulation i.e. the maintenance of homeostasis of the body. Hence, excretion is a necessary process of our trunk.
(b) If ane kidney is donated to a needy patient, the other kidney alone is sufficient for removing wastes or excretion. Thus, the donor tin can live a normal life.
(c) During summer, a considerable part of water is lost through perspiration so the kidneys have to reabsorb more water from the urine. This makes the urine thicker in summer than in winters.
Question D.4
What is a uriniferous tubule? How does information technology function?
Solution D.iv
A uriniferous tubule as well known equally the kidney tubule is the structural and functional unit of the kidney.
It takes in impure blood from the renal avenue and removes wastes in the form of urine. Information technology too provides a larger surface expanse for reabsorption of salts and water.
Question D.5
Why is it necessary to maintain a normal osmotic concentration of the blood?
Solution D.five
Maintaining a normal osmotic concentration in the body means regulating the percentage of water and salts. If this regulation mechanism fails nosotros either terminate upwardly losing vital salts and water or may accumulate unwanted salts and backlog water in our body.
Question D.6
Explain the terms ultrafiltration and selective absorption.
Solution D.six
Ultrafiltration -
Ultrafiltration involves filtration of the blood which takes identify in the glomerulus. The blood containing urea from the afferent arteriole enters the glomerulus under high pressure. The high pressure is created because the efferent arteriole is narrower than the afferent arteriole. The loftier pressure level causes the liquid part of the blood to filter out from the glomerulus into the renal tubule. This filtrate is known as 'glomerular filtrate'.
Glomerular filtrate consists of water, urea, salts, glucose and other plasma solutes. Blood corpuscles, proteins and other large molecules remain behind in the glomerulus. Therefore the blood which is carried abroad by the efferent arteriole is relatively thick.
Selective assimilation
The Glomerular filtrate inbound the renal tubule contains a lot of usable materials such as glucose and sodium. Every bit this filtrate passes downward the renal tubule, a lot of water along with these usable materials is reabsorbed. Such reabsorption is called 'selective absorption'. The reabsorption occurs only to the extent that the normal concentration of the blood is undisturbed.
Question D.7
What is dialysis? Under what conditions is information technology carried out?
Solution D.7
Dialysis involves the use of artificial kidney or a dialysis auto. The patient'south claret is from the radial avenue is led through the machine where backlog salts and urea is removed. The purified claret is so returned to a vein in the same arm.
Dialysis is carried out in case of failure of both the kidneys. In case there is a permanent damage, so the dialysis is to be repeated for about 12 hours twice a week.
Question E.1
Look at the figure given below. It is a section of man kidney as seen from the front.
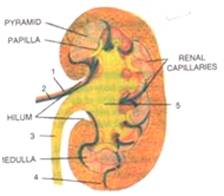
(a) Is it a longitudinal section or a cross-section?
(b) Name the parts numbered 1-v.
(c) Which area/role (requite its proper noun and number given on the diagram) which contains the following:
(i) Malpighian sheathing
(ii) "The pyramids" to The claret vessel with least/no nitrogenous waste
(three) Freshly collected urine
Solution E.1
(a) Information technology is a longitudinal department of the kidney.
(b) ane-renal avenue, 2-renal vein, 3-ureter, 4-cortex, 5-pelvis
(c) (i) four/cortex
(ii) medulla
(iii)5/pelvis
Question E.2
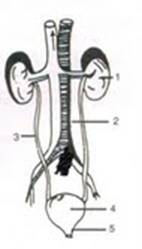
Given below is the figure of certain organs and associated parts in the human being body. Study the aforementioned and answer the questions that follow:
(a) Name all the organ-systems shown completely or even partially.
(b) Proper noun the parts numbered 1 to 5.
(c) Name the structural and functional unit of the part marked 'ane'.
(d) Name the two main organic constituents of the fluid that flows downward the part labeled '3'.
(e) Proper name the two major steps involved in the formation of the fluid that passes downward the part labeled '3'.
Solution E.2
(a) Excretory system and Circulatory system.
(b) ane-kidney, ii-renal artery, 3-ureter, 4-urinary float, 5-urethera
(c) Nephron
(d) Urea and ammonia
(e) Ultrafiltration and selective reabsorption
Question E.3
The following diagram represents a mammalian kidney tubule (nephron) and its blood supply.
Parts indicated by the guidelines i to viii are as follows:
1. Afferent arteriole from renal artery
2. Efferent arteriole
iii. Bowman'south sheathing
4. Glomerulus
five. Proximal convoluted tubule with blood capillaries
6. Distal convoluted tubule with blood capillaries
7. Collecting tubule
8. U-shaped loop of Henle
Study the diagram and reply the questions that follow:
(a) Where does ultrafiltration take place?
(b) Which structure contains the everyman concentration of urea?
(c) Which structure contains the highest concentration of urea?
(d) Which structure (normally) contains the lowest concentration of glucose?
(eastward) Where is most h2o reabsorbed?
(f) State the reason for the high hydrostatic pressure in the glomerulus.
(g) Name the part of the nephron which lies in the renal medulla.
Solution E.3
(a) 4 / Glomerulus
(b) 2 / Efferent arteriole
(c) one / Afferent arteriole from renal avenue
(d) 7 / Collecting tubule
(eastward) 5 / Proximal convoluted tubule with blood capillaries
(f) The efferent arteriole is narrower than the afferent arteriole. This creates a high hydrostatic force per unit area in the glomerulus.
(g) Loop of Henle
Question Eastward.4
Given alongside is a simplified diagram of the human kidney cut open up longitudinally. Answer the questions that follow:
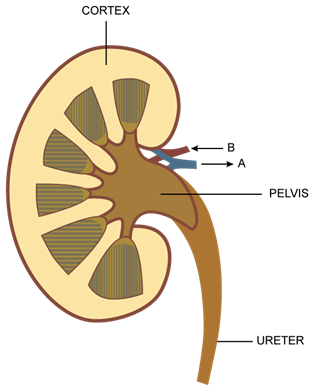
(a) Define excretion.
(b) Why does the cortex of the kidney show a dotted appearance?
(c) Why does the medulla of the kidney bear witness a striped advent?
(d) Write two differences in limerick of the blood flowing through the blood vessels, 'A' and 'B'.
Solution E.4
(a) The process of removal of chemic wastes especially nitrogenous waste matter from the body is known every bit excretion.
(b) Equally the cortex region contains numerous nephrons or kidney tubules, therefore, information technology shows a dotted advent.
(c) As the medulla region contains several conical pyramids, therefore, it shows a striped appearance.
(d) The claret vessel 'B' is renal artery and the blood vessel 'A' is renal vein. So the blood vessel 'B' contains oxygenated blood with high concentration of urea and glucose whereas the blood vessel 'A' contains deoxygenated blood with low concentration of urea and glucose as compared to renal artery.
Question Due east.five
Study the diagram given alongside and and so respond the questions that follow:
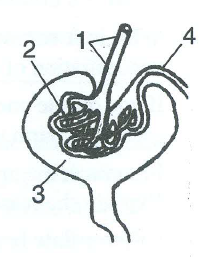
a. Name the region in the kidney where the above structure is present?
b. Proper noun the parts labelled 1, two, 3, and 4.
c. Proper name the stages involved in the formation of urine.
d. What is the technical term given to the process occurring in two and iii? Briefly describe the procedure.
Solution E.five
a. The structure is a Bowman's capsule, which is role of the nephron. The Bowman'due south capsule is found in the cortex of the kidney.
b.
1 - Afferent arteriole
2 - Glomerulus
3 - Bowman'southward capsule
4 - Efferent arteriole
c. Urine formation occurs in ii steps - ultrafiltration and reabsorption.
d. The procedure occurring in 2 and 3 is known as ultrafiltration.
In the glomerulus, the blood flows under high pressure because of the narrow lumen of the capillary network of the glomerulus. This forces nearly of the components (both waste and useable materials) of the blood out of the capillaries. This process of the filtration of claret nether high pressure in the Bowman'south capsule is known equally ultrafiltration.
Question E.vi
The given diagram represents a nephron and its blood supply. Report the diagram and respond the following questions:
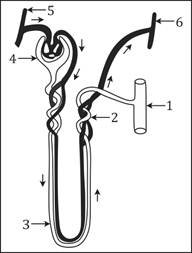
(a) Label parts 1, ii, 3 and 4.
(b) State the reason for the high hydrostatic pressure in the glomerulus.
(c) Name the blood vessel which contains the least amount of urea in this diagram.
(d) Proper noun the two main stages of urine formation.
(e) Proper noun the function of the nephron which lies in the renal medulla.
Solution E.6
(a) ane - Collecting duct
ii - Distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
iii - Descending limb of loop of Henle
four - Bowman'due south capsule
(b) The diameter of the efferent arteriole is narrower than the bore of the afferent arteriole which builds loftier hydrostatic force per unit area in the glomerulus.
(c) Efferent arteriole
(d) Two main stages of urine formation are ultrafiltration and tubular reabsorption.
(e) Henle'southward loop and collecting tubules
Source: https://www.topperlearning.com/selina-solutions/icse-class-10-biology/selina-concise-biology-part-ii/the-excretory-system
0 Response to "Chapter 9 and 11 Worksheet Answers Biology Review"
Enregistrer un commentaire